Variables and Data Types
Introduction to Variables
Let's create a new Python file called variables by again right-clicking first-pycharm-project and clicking on New > Python file. Like before, we'll enter the desired name in the window that pops up. I have chosen the name variables.py.
Now with our blank variables.py file we can begin to learn what variables are about.
Why Use Variables?
Python allows us to perform calculators with whole-numbers. In programming, we refer to these whole-number values as integers or ints.
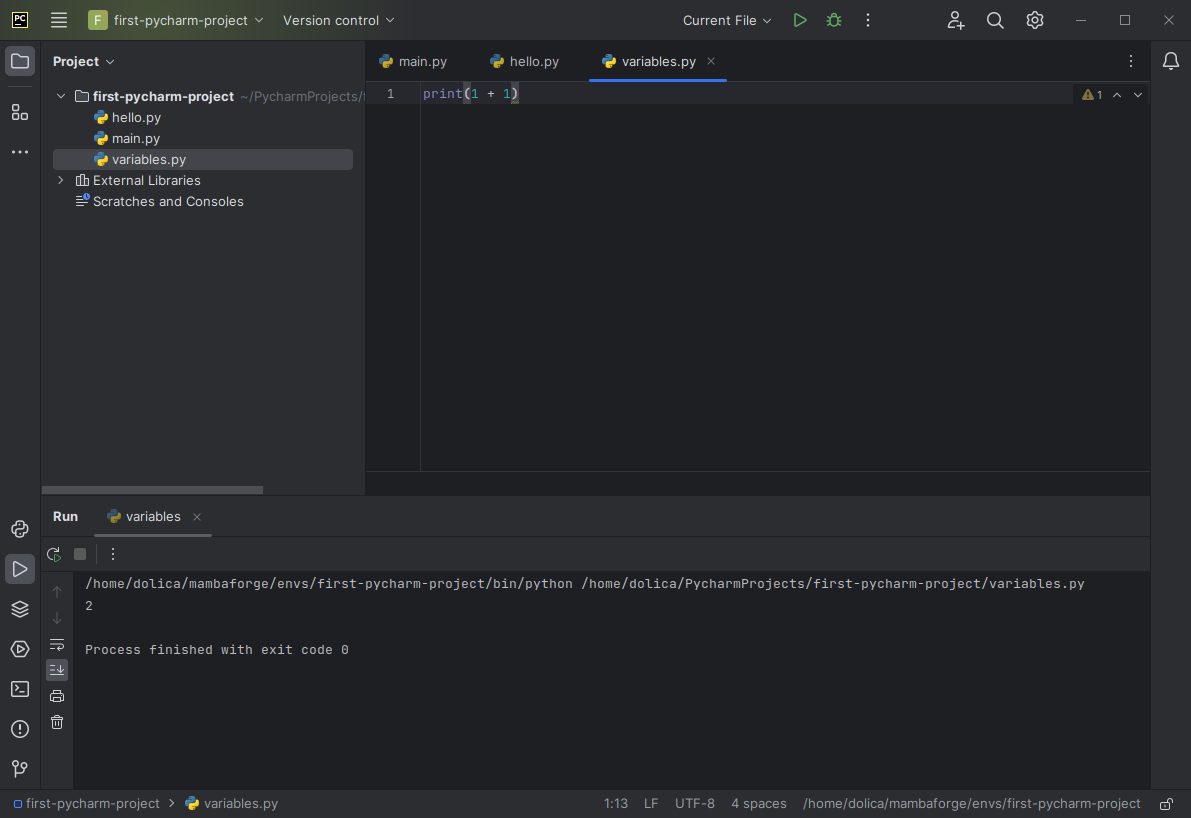
Let's say we want to use Python to add two whole-numbers. We can use Python as a calculator. Try entering the following code in your variables.py file and running it.
print(1 + 1)
As you'd expect, Python tells us that 1 + 1 gives a result of 2.
However, rather than simply print of such values once, we may want to store the results of a more complex calculation so that it can be used or modified later. This is when we would use something called a variable.
What Are Variables?
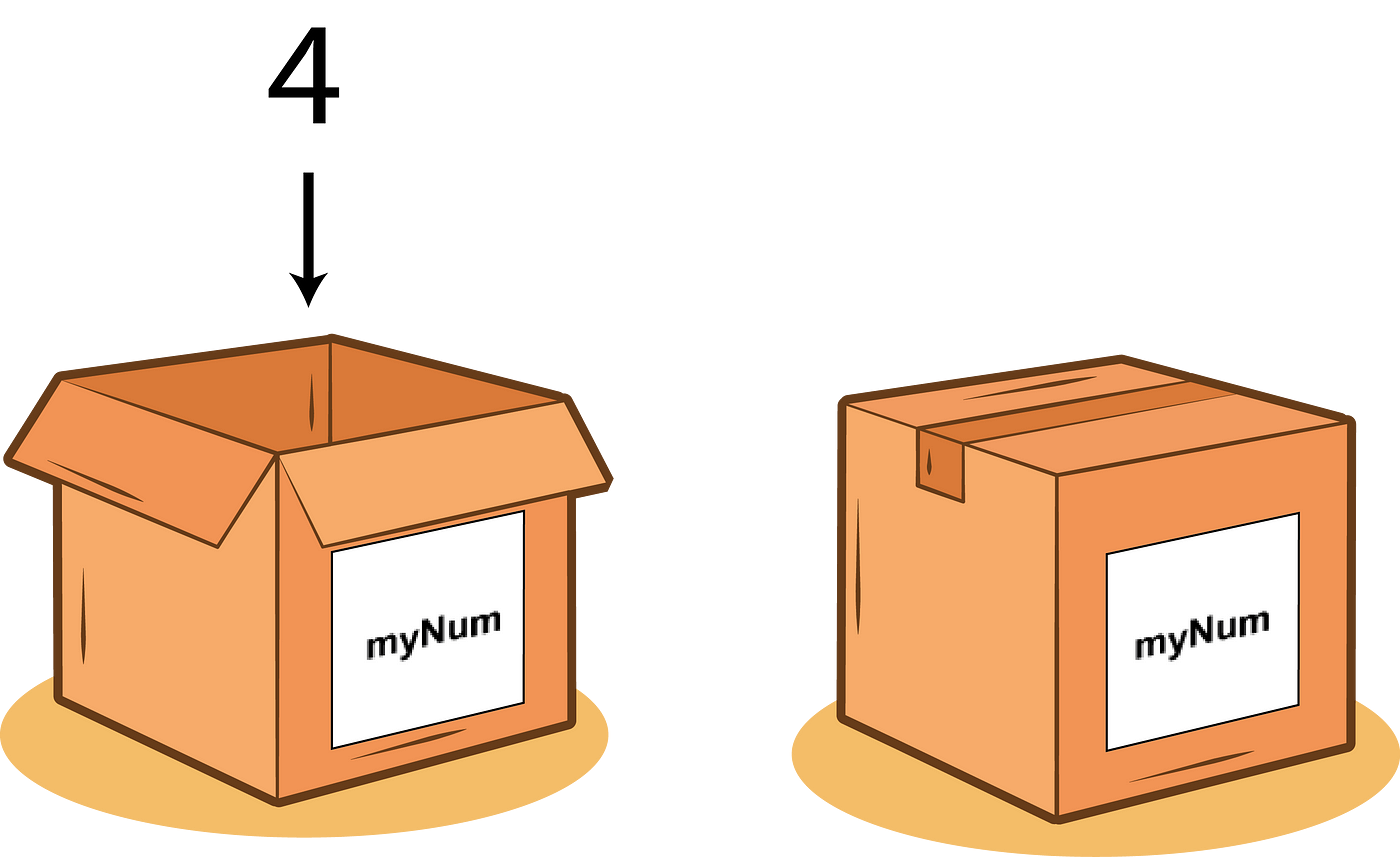
In the world of programming, variables are like containers that hold information. Imagine them as labeled boxes where you can store different types of data. These data could be numbers, words, sentences, or anything else your program needs to work with.
Variables allow you to give a name to a piece of data, making our code more readable and organised.
Variable Assignment
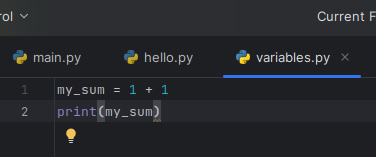
To put data into a variable, we use the assignment operator =. Now we can find our 1 + 1 and store the result.
my_sum = 1 + 1
But this alone won't display the result when we run the program. In order to this we will use another print() statement, but give it our my_sum variable.
Put together, we get the following two lines of code: