How to send data to p5.js from Arduino
What is the Serial Communication?
Serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. Simply put, serial communication is the communication between two or more computers with binary data.
In this tutorial, we will use serial communication protocol to send data to Processingp5.js from Arduino.Arduino using the P5.js WebSerial Library. The Processingp5.js sketch will be controlled by the physical component, the ultrasonic sensor,potentiometer, which can be replaced with other sensors, button and etc.
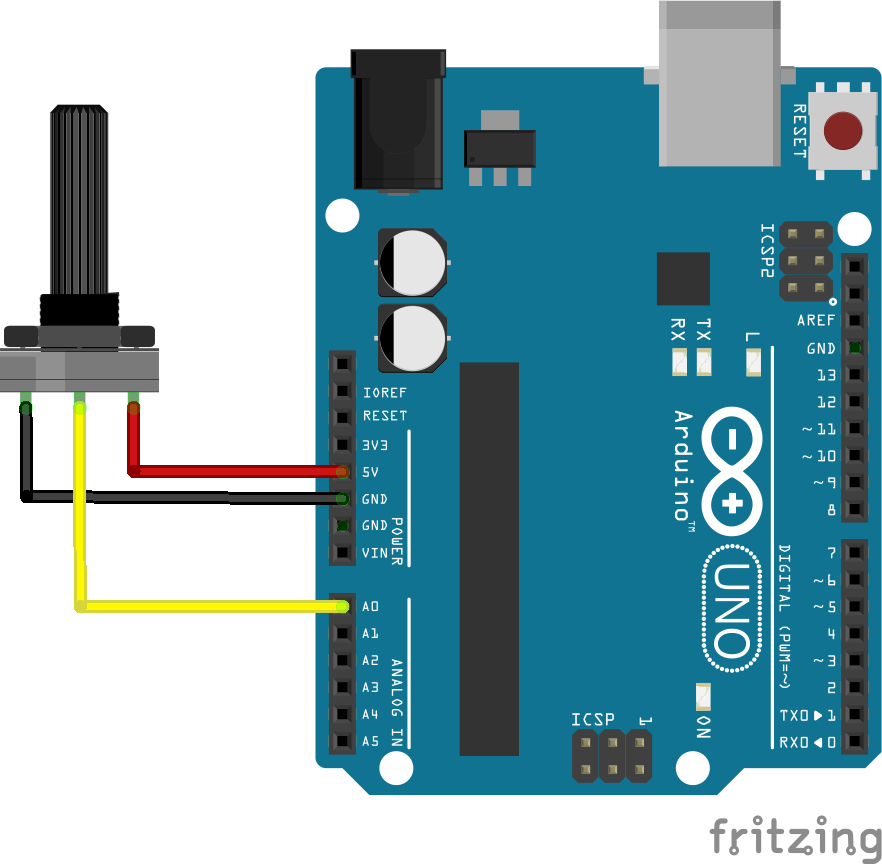
Wiring
- Left pin to 5V
- Right pin to GND
- middle pin to A0
Arduino Code
This example sends the distancepotentiometer value measured from Arduino to Processingp5.js via the serial port, you can read the data from the serial monitor.
#define potPin A0
int value;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //intailise Serial communication with 9600 baud rate
pinMode( potPin, INPUT );
}
void loop() {
value = analogRead( potPin);
Serial.println(value); //read the sensor and send the value to the Serial
delay(100); //little delay to prevent Arduino going crazy
}
Processingp5.js Code
This example usedwill show the incoming data received from Arduino to controlon the degreescanvas.
A rotationp5.js sketch is actually a website that consists of a rectanglehtml file, a css file and a java script which makes everything fun.
To access different files in Processing.your sketch, you can click the arrow and the panel on the left will show the files associated with the sketch.
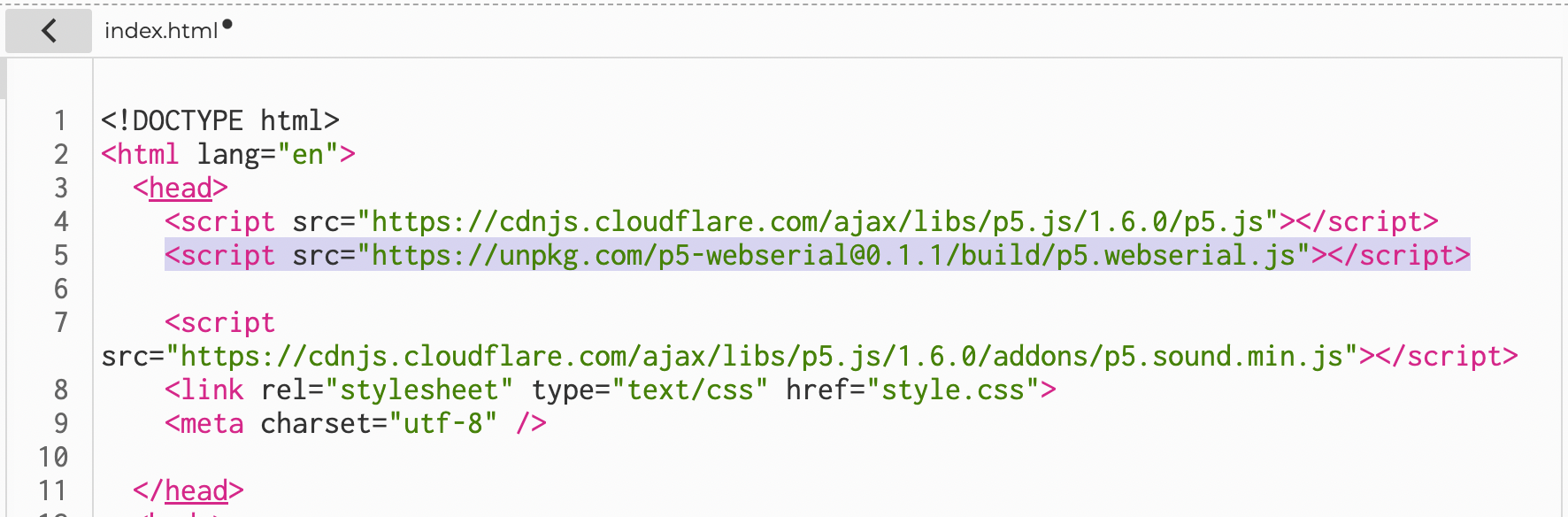
First we have to install the P5.js WebSerial Library.
You have to place the below script in the index.html file, inside the head.
import<script processing.serial.*src="https://unpkg.com/p5-webserial@0.1.1/build/p5.webserial.js"></script>
The below is the example code that should be placed in the sketch.js file. Please read the comments in the code to understand what they do.
// variable to hold an instance of the p5.webserial library:
const serial = new p5.WebSerial();
Serial// myPort;HTML Stringbutton val;object:
intlet datanumportButton;
let inData; // for incoming serial data
let outByte = 0; //number offor outgoing data
receivinglet fromvals Arduino= int[];
value1;
//int value2; //multiple data from arduino if needed
voidfunction setup() {
size(800,createCanvas(400, 800)300); printArray(Serial.list(// make the canvas
// check to see if serial is available:
if (!navigator.serial) {
alert("WebSerial is not supported in this browser. Try Chrome or MS Edge.");
}
// if serial is available, add connect/disconnect listeners:
navigator.serial.addEventListener("connect", portConnect);
navigator.serial.addEventListener("disconnect", portDisconnect);
// check for any ports that are available:
serial.getPorts();
//show allif portsthere's String portName = Serial.list()[0];//choose the correctno port myPortchosen, =choose newone:
Serial(this,serial.on("noport", portName, 9600)makePortButton);
myPort.bufferUntil('\n')// open whatever port is available:
serial.on("portavailable", openPort);
// handle serial errors:
serial.on("requesterror", portError);
// handle any incoming serial data:
serial.on("data", serialEvent);
serial.on("close", makePortButton);
}
voidfunction draw() {
background(0);
fill(255);
text("sensor value: " + inData, 30, 50);
}
//map() isif there's no port selected,
// make a importantport select button appear:
function tomakePortButton() use here,{
//it convert the raw data range from Arduino to the ideal range to use in Processing
//map(a, b, c, d, e) has 5 Parameters
//map(theVariableYouWantToMap, min.ValueOfRawData, max.ValueOfRawData, min.ValueOfIdealRange, max.ValueOfIdealRange)
//in this case the min. value from the pot is 0create and max.position valuea isport 1023.chooser //andbutton:
I want to map the background colour from black to white, 0(black) - 255(white)
float BWportButton = map(value1,0,createButton("choose 1023,port");
0,portButton.position(10, 255 )10);
//create give the port button a variablemousepressed tohandler:
contain the converted value
background(BW)portButton.mousePressed(choosePort);
}
void// serialEvent(make Serialthe myPort)port selector window appear:
function choosePort() {
val = myPort.readStringUntil('\n');
if (valportButton) portButton.show();
serial.requestPort();
}
// open the selected port, and make the port
// button invisible:
function openPort() {
// wait for the serial.open promise to return,
// then call the initiateSerial function
serial.open().then(initiateSerial);
// once the port opens, let the user know:
function initiateSerial() {
console.log("port open");
}
// hide the port button once a port is chosen:
if (portButton) portButton.hide();
}
// pop up an alert if there's a port error:
function portError(err) {
alert("Serial port error: " + err);
}
// read any incoming data as a string
// (assumes a newline at the end of it):
function serialEvent() {
inData = serial.readLine();
if(inData != null)
{
valinData = trim(val)inData);
int[]
vals = int(splitTokens(val,inData, ","));
if(vals.length >= datanum)1){
value1 = vals[0];
//multiple data from arduino if needed
//value2 = vals[1] ;
print(console.log(value1);
}
}
}
// try to connect if a new serial port
// gets added (i.e. plugged in via USB):
function portConnect() {
console.log("port connected");
serial.getPorts();
}
// if a port is disconnected:
function portDisconnect() {
serial.close();
console.log("port disconnected");
}
function closePort() {
serial.close();
}