Using an PN532 RFID reader
What is the difference between an PN532 RFID reader and an MFRC522 RFID reader
RFIDThe meansPN532 radio-frequencyand identification.MFRC522 are two popular RFID usesreader electromagneticmodules, fieldseach with its own features and use cases.

| Feature | PN532 | MFRC522 |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | SPI, I2C, UART | SPI only |
| Supported Protocols | NFC, RFID (13.56 MHz) | RFID (13.56 MHz) |
| Standards | ISO14443A/B, FeliCa | ISO14443A (MIFARE) |
| Range | ~10 cm | ~5 cm |
| Cost | Higher (~$10–$30) | Lower (~$2–$10) |
| Power | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Advanced, NFC, IoT | Basic RFID projects |
| Module | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| PN532 |
|
|
| MFRC522 |
|
|
In this tutorial, we will be using a PN532 module from DFRobot, if you are using an MFRC522 module, please refer to makethis transactions, etc…tutorial.
YouThis cantutorial useis anadapted from here.
RFID systemTag
Aside open a door. For example, onlyfrom the personregular withcard, thethere rightare informationmore onoptions histhan cardbefore, isincluding allowedstickers, to enter. An RFID system usesbutton tags with each identification and a two-way radio transmitter-receiver as a reader.etc.
Wiring
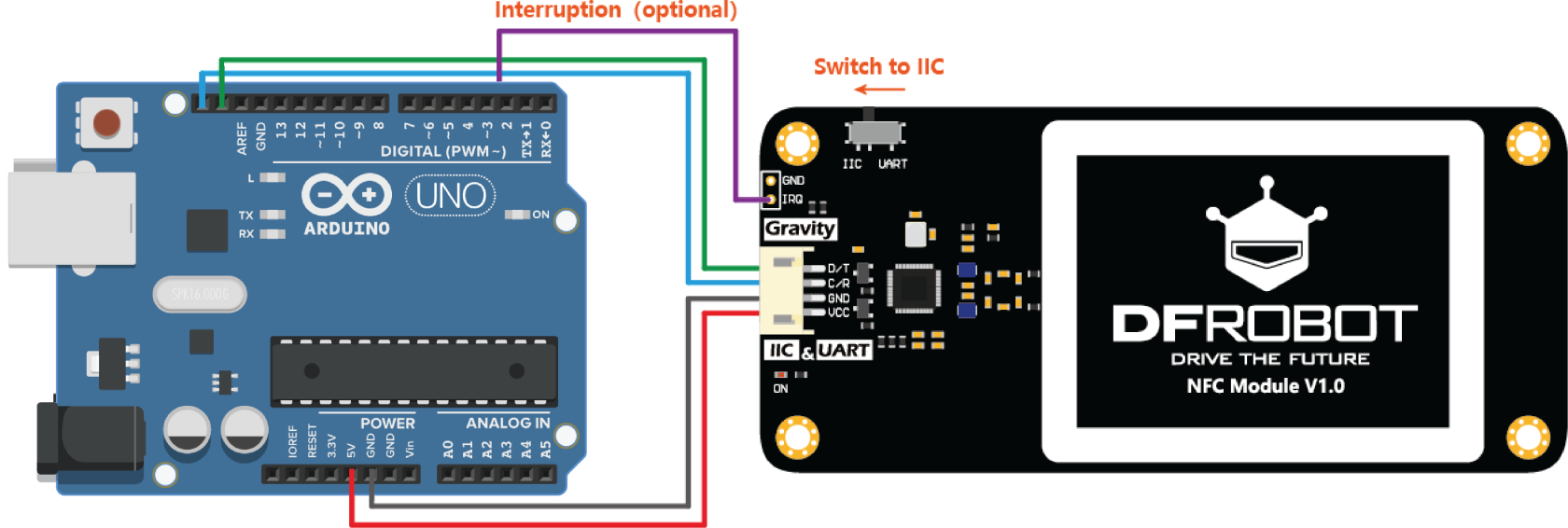
CautionSwitch
You must power this device to 3.3V!
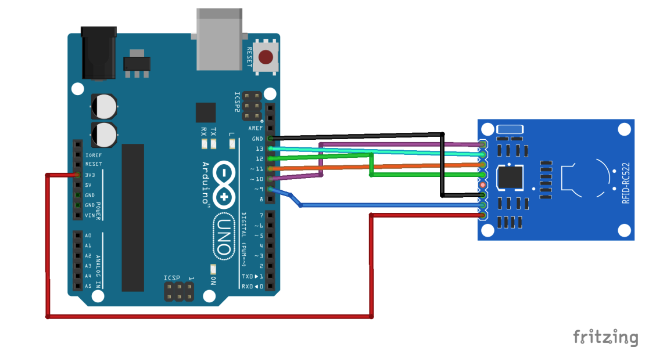
This tutorial iswill basedbe using the i2c communication protocol, make sure you switch to IIC on Arduino UNO, if you are using a different module, please check the specific pinout of that model.module.
SDAD/T -Digital 10SDA (SS)Pin 14)SCKC/R -Digital 13SCL (SCK)Pin MOSI - Digital 11 (MOSI)MISO - Digital 12 (MISO)IRQ (unconnected)15)- GND - GND (Ground)
RST - Digital 93.3VVCC to3.3V5V (Power)
Library
We will be using the MFRC522DFRobot_PN532
Getting started
WeThe number of blocks of data depends on the type of RFID tag or card you’re using. Most commonly, the MIFARE Classic card is used, which is compatible with both the PN532 and MFRC522. A standard MIFARE Classic 1K card will behave using64 blocks of data and the examplesmaller code,NTAG213 DumpInfo,tag will have 36 blocks of data.
Some blocks are read-only, so you cannot write data to those blocks. For example, Block 0 usually contains the UID (Unique Identifier) and other manufacturer data, and is read-only.
The below codes are only for writing to and reading the data from theBlock library3.
Write read an RFID Tag.Data
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.DFRobot_PN532.h>
#define RST_PINBLOCK_SIZE 916
#define PN532_IRQ 2
#define INTERRUPT 1
#define POLLING 0
// Configurable,The seeblock typicalto pinbe layout abovewritten
#define SS_PINWRITE_BLOCK_NO 103
//DFRobot_PN532_IIC Configurable,nfc(PN532_IRQ, seePOLLING);
typicaluint8_t pindataWrite[BLOCK_SIZE] layout= above{"your MFRC522 mfrc522(SS_PIN, RST_PIN)message"}; //change Createto MFRC522your instancedata
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600)115200);
// Initialize serial communications with the PCSerial.print("Initializing");
while (!Serial)nfc.begin()) {
Serial.print(".");
// Do nothing if no serial port is openeddelay (added1000);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Waiting for Arduinosa based on ATMEGA32U4)
SPI.begin(); // Init SPI bus
mfrc522.PCD_Init(); // Init MFRC522
delay(4); // Optional delay. Some board do need more time after init to be ready, see Readme
mfrc522.PCD_DumpVersionToSerial(); // Show details of PCD - MFRC522 Card Reader details
Serial.println(F("Scan PICC to see UID, SAK, type, and data blocks.card......"));
}
void loop() {
// ResetFor S50 card/tag, block 1-2, 4-6, 8-10, 12-14... 56-58, 60-62 are for user data
// You can read/write these blocks freely.
// Use "MifareClassic_ReadAllMemory.ino" to check all the loop if no new card is present on the sensor/reader. This saves the entire process when idle.blocks
if ( ! mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent(nfc.scan()) {
return;if (nfc.writeData(WRITE_BLOCK_NO, dataWrite) != 1) {
Serial.print("Block ");
Serial.print(WRITE_BLOCK_NO);
Serial.println(" write failure!");
}
//else Select{
oneSerial.print("Block of");
theSerial.print(WRITE_BLOCK_NO);
cardsSerial.println(" ifwrite success!");
Serial.print("Data written(string):");
Serial.println((char *)dataWrite);
Serial.print("Data written(HEX):");
for (int !i mfrc522.PICC_ReadCardSerial()= 0; i < BLOCK_SIZE; i++) {
return;Serial.print(dataWrite[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
//}
Dump}
debug info about the card; PICC_HaltA() is automatically called
mfrc522.PICC_DumpToSerial(&(mfrc522.uid))delay(500);
}
We
Read willData
#include <DFRobot_PN532.h>
#define BLOCK_SIZE 16
#define PN532_IRQ 2
#define INTERRUPT 1
#define POLLING 0
// The block to be usingread
#define READ_BLOCK_NO 3
DFRobot_PN532_IIC nfc(PN532_IRQ, POLLING);
uint8_t dataRead[16] = {0};
void setup() {
pinMode(13,OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.print("Initializing");
while (!nfc.begin()) {
Serial.print(".");
delay (1000);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Waiting for a card......");
}
void loop() {
// For S50 card/tag, block 1-2, 4-6, 8-10, 12-14... 56-58, 60-62 are for user data
// You can read/write these blocks freely.
// Use "MifareClassic_ReadAllMemory.ino" to check all the exampleblocks
code,if DumpInfofromHEX);
theSerial.print(" library");
todataRead[i] read= an0;
RFID}
Tag.Serial.println();
*/
}
delay(500);
}
}