Using an PN532 RFID reader
What is the difference between an PN532 RFID reader and an MFRC522 RFID reader
The PN532 and MFRC522 are two popular RFID reader modules, each with its own features and use cases.

| Feature | PN532 | MFRC522 | Which Better |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication | SPI, I2C, UART | SPI only | ✔ PN522 |
| Supported Protocols | NFC, RFID (13.56 MHz) | RFID (13.56 MHz) | ✔ PN522 |
| Standards | ISO14443A/B, FeliCa | ISO14443A (MIFARE) | ✔ PN522 |
| Range | ~10 cm | ~5 cm | ✔ PN522 |
| Cost | Higher (~$10–$30) | Lower (~$2–$10) | ✔ MFRC522 |
| Power | Higher | Lower | ✔ MFRC522 |
| Applications | Advanced, NFC, IoT | Basic RFID projects | ✔ PN522 |
In this tutorial, we will be using a PN532 module from DFRobot, if you are using an MFRC522 module, please refer to this tutorial. This tutorial is adapted from here.
RFID Tag
Aside from the regular card, there are more options than before, including stickers, button tags etc.
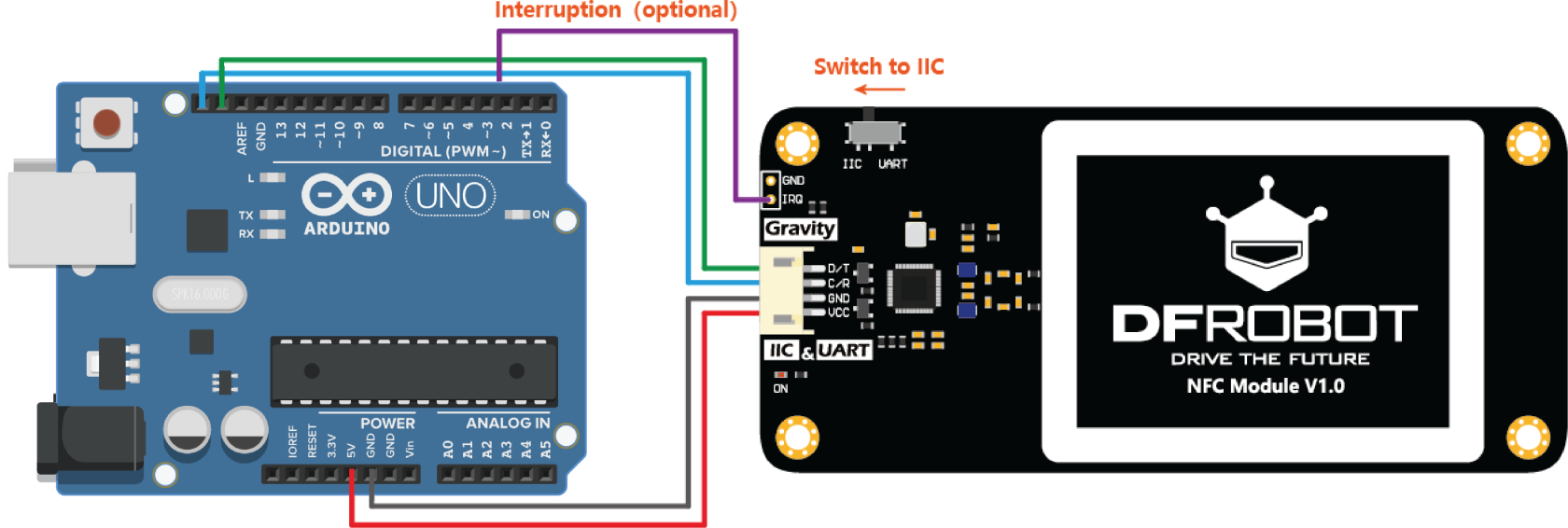
Wiring
Switch
This tutorial will be using the i2c communication protocol, make sure you switch to IIC on the module.
- D/T - SDA (Pin 14)
- C/R - SCL (Pin 15)
- GND - GND (Ground)
- VCC to 5V (Power)
Library
We will be using the DFRobot_PN532 library. Please see this tutorial to learn how to install libraries.
Getting started
The number of blocks of data depends on the type of RFID tag or card you’re using. Most commonly, the MIFARE Classic card is used, which is compatible with both the PN532 and MFRC522. A standard MIFARE Classic 1K card will have 64 blocks of data and the smaller NTAG213 tag will have 36 blocks of data.
Some blocks are read-only, so you cannot write data to those blocks. For example, Block 0 usually contains the UID (Unique Identifier) and other manufacturer data, and is read-only.
The below codes are only for writing to and reading the data from Block 3.
Write Data
#include <DFRobot_PN532.h>
#define BLOCK_SIZE 16
#define PN532_IRQ 2
#define INTERRUPT 1
#define POLLING 0
// The block to be written
#define WRITE_BLOCK_NO 3
DFRobot_PN532_IIC nfc(PN532_IRQ, POLLING);
uint8_t dataWrite[BLOCK_SIZE] = {"your message"}; //change to your data
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.print("Initializing");
while (!nfc.begin()) {
Serial.print(".");
delay (1000);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Waiting for a card......");
}
void loop() {
// For S50 card/tag, block 1-2, 4-6, 8-10, 12-14... 56-58, 60-62 are for user data
// You can read/write these blocks freely.
// Use "MifareClassic_ReadAllMemory.ino" to check all the blocks
if (nfc.scan()) {
if (nfc.writeData(WRITE_BLOCK_NO, dataWrite) != 1) {
Serial.print("Block ");
Serial.print(WRITE_BLOCK_NO);
Serial.println(" write failure!");
}
else {
Serial.print("Block ");
Serial.print(WRITE_BLOCK_NO);
Serial.println(" write success!");
Serial.print("Data written(string):");
Serial.println((char *)dataWrite);
Serial.print("Data written(HEX):");
for (int i = 0; i < BLOCK_SIZE; i++) {
Serial.print(dataWrite[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
}
}
delay(500);
}
Read Data
#include <DFRobot_PN532.h>
#define BLOCK_SIZE 16
#define PN532_IRQ 2
#define INTERRUPT 1
#define POLLING 0
// The block to be read
#define READ_BLOCK_NO 3
DFRobot_PN532_IIC nfc(PN532_IRQ, POLLING);
uint8_t dataRead[16] = {0};
void setup() {
pinMode(13,OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.print("Initializing");
while (!nfc.begin()) {
Serial.print(".");
delay (1000);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Waiting for a card......");
}
void loop() {
// For S50 card/tag, block 1-2, 4-6, 8-10, 12-14... 56-58, 60-62 are for user data
// You can read/write these blocks freely.
// Use "MifareClassic_ReadAllMemory.ino" to check all the blocks
if (nfc.scan()) {
if (nfc.readData(dataRead, READ_BLOCK_NO) != 1) {
Serial.print("Block ");
Serial.print(READ_BLOCK_NO);
Serial.println(" read failure!");
}
else {
Serial.print("Block ");
Serial.print(READ_BLOCK_NO);
Serial.println(" read success!");
Serial.print("Data read(string):");
String data = (char *)dataRead;
Serial.println(data);
/*
//interaction
if(data == "your message" ){
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
}else{
digitalWrite(13, LOW);
}
*/
/*
//in hex
Serial.print("Data read(HEX):");
for (int i = 0; i < BLOCK_SIZE; i++) {
Serial.print(dataRead[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
dataRead[i] = 0;
}
Serial.println();
*/
}
delay(500);
}
}
NTAG203
If you are using a NTAG203 sticker, you will need to use the Adafruit_PN532 library instead.
Write Data
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_PN532.h>
#define SDA_PIN SDA
#define SCL_PIN SCL
#define WRITE_PAGE_NO 4 // Change this to the correct writable page
Adafruit_PN532 nfc(SDA_PIN, SCL_PIN);
uint8_t dataWrite[4] = {'T', 'E', 'S', 'T'}; // Must be 4 bytes for NTAG203
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
nfc.begin();
uint32_t versiondata = nfc.getFirmwareVersion();
if (!versiondata) {
Serial.println("PN532 not found!");
while (1);
}
nfc.SAMConfig();
Serial.println("Waiting for an NFC card...");
}
void loop() {
uint8_t uid[] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}; // Store UID
uint8_t uidLength;
if (nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, uid, &uidLength)) {
Serial.println("NFC tag detected!");
if (nfc.ntag2xx_WritePage(WRITE_PAGE_NO, dataWrite)) {
Serial.println("Write successful!");
} else {
Serial.println("Write failed!");
}
delay(2000); // Avoid continuous writes
}
}
Read Data
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_PN532.h>
#define SDA_PIN SDA
#define SCL_PIN SCL
#define READ_PAGE_NO 4 // Change this to the page you want to read
Adafruit_PN532 nfc(SDA_PIN, SCL_PIN);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
nfc.begin();
uint32_t versiondata = nfc.getFirmwareVersion();
if (!versiondata) {
Serial.println("PN532 not found!");
while (1);
}
nfc.SAMConfig();
Serial.println("Waiting for an NFC tag...");
}
void loop() {
uint8_t uid[] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}; // To store the tag UID
uint8_t uidLength;
if (nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, uid, &uidLength)) {
Serial.println("NFC tag detected!");
uint8_t dataRead[4]; // NTAG203 pages are 4 bytes each
if (nfc.ntag2xx_ReadPage(READ_PAGE_NO, dataRead)) {
Serial.print("Data at Page ");
Serial.print(READ_PAGE_NO);
Serial.print(": ");
// Print as ASCII characters
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Serial.print((char)dataRead[i]);
}
Serial.print(" (HEX: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Serial.print(dataRead[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println(")");
} else {
Serial.println("Read failed!");
}
delay(2000); // Avoid continuous reads
}
}