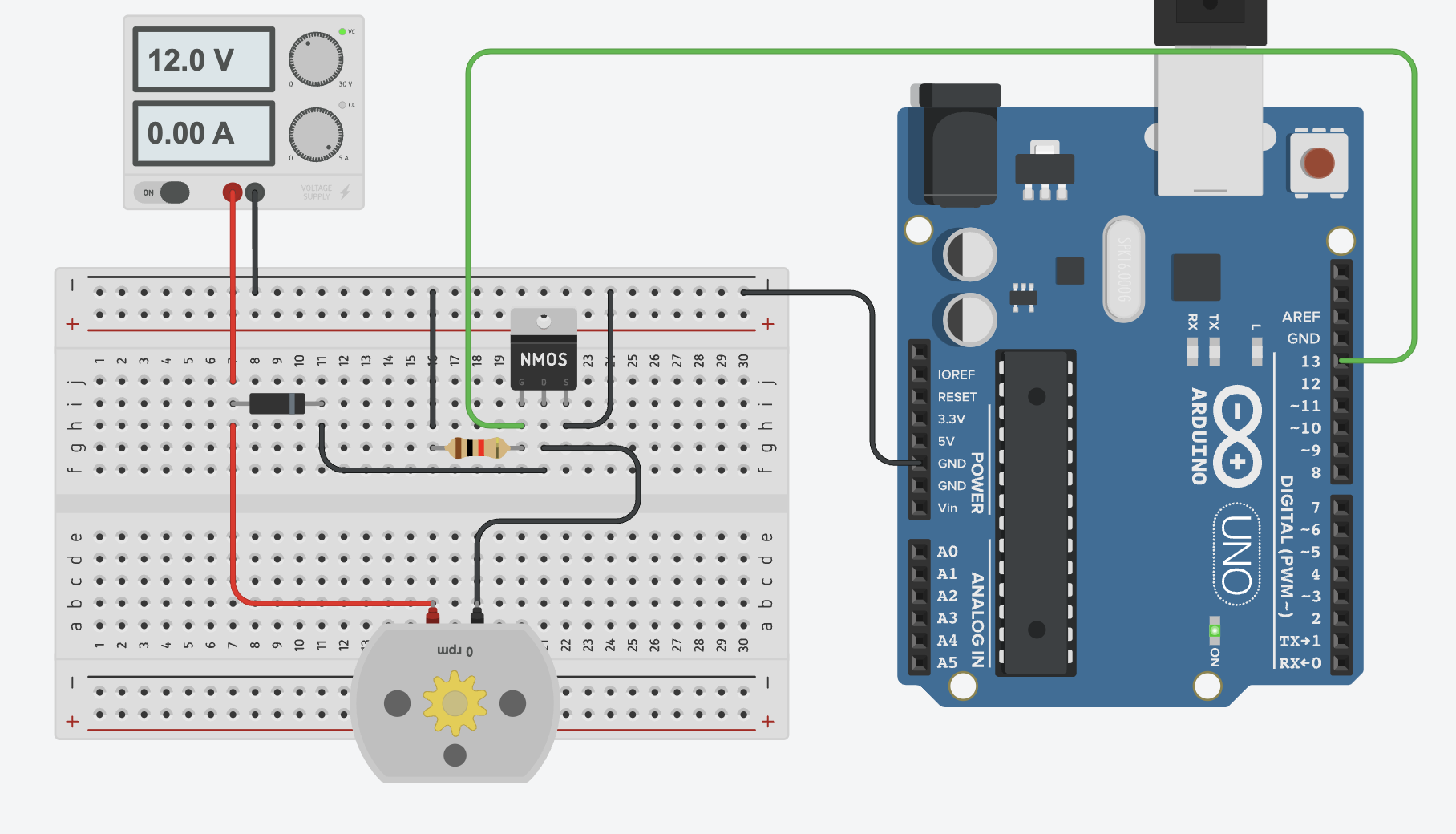
Controlling an actuator with a N-channel Mosfet
What is Mosfet?
A MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) is a type of transistor used to switch or amplify electrical signals in electronic devices. It’s one of the most common components in electronic circuits, especially in digital and analog systems.
Structure
A MOSFET has three main terminals — Gate, Drain, and Source. The Gate is separated from the channel by a thin insulating layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Operation
A small voltage applied to the Gate controls the current flow between the Drain and Source terminals. By adjusting this voltage, the MOSFET can act as a switch (turning the current on or off) or as an amplifier (controlling the level of current flow).
Types
There are two main types of MOSFETs, we will be using a N-channel Mosfet in this tutorial.e
- N-channel MOSFETs: These conduct when a positive voltage is applied to the Gate relative to the Source.
- P-channel MOSFETs: These conduct when a negative voltage is applied to the Gate relative to the Source.
Wiring
- Source (S) to
GND - Drain (D) to
actuator(-)& todiode(-) - Gate (G) to
GNDvia 1k resistor & toPin 13 - Power Supply(+) to
actuator(+)&diode(+) - Power Supply(-) to
GND
Basic Example
This basic example is effectively the blink sketch, the TinkerKit Mosfet operates just like any other digital device.
#define actuatorPin 13
void setup() {
pinMode( actuatorPin, OUTPUT );
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite( actuatorPin, HIGH );
delay( 1000 );
digitalWrite( actuatorPin, LOW );
delay( 1000 );
}