Making a Force Sensor/ a Button with Velostat & Conductive Fabric
What is a Velostat and Conductive Fabric?
Velostat (a.k.a. Linqstat) is a thin, flexible, pressure-sensitive plastic sheet made with carbon black. It’s a piezoresistive material — its electrical resistance changes when pressure is applied.
Conductive Fabric is a textile material (woven or non-woven) with conductive threads or coatings, like silver, copper, nickel, or carbon. It conducts electricity like a wire but is soft and flexible like fabric.
Assembling the Velostat and Conductive Fabric
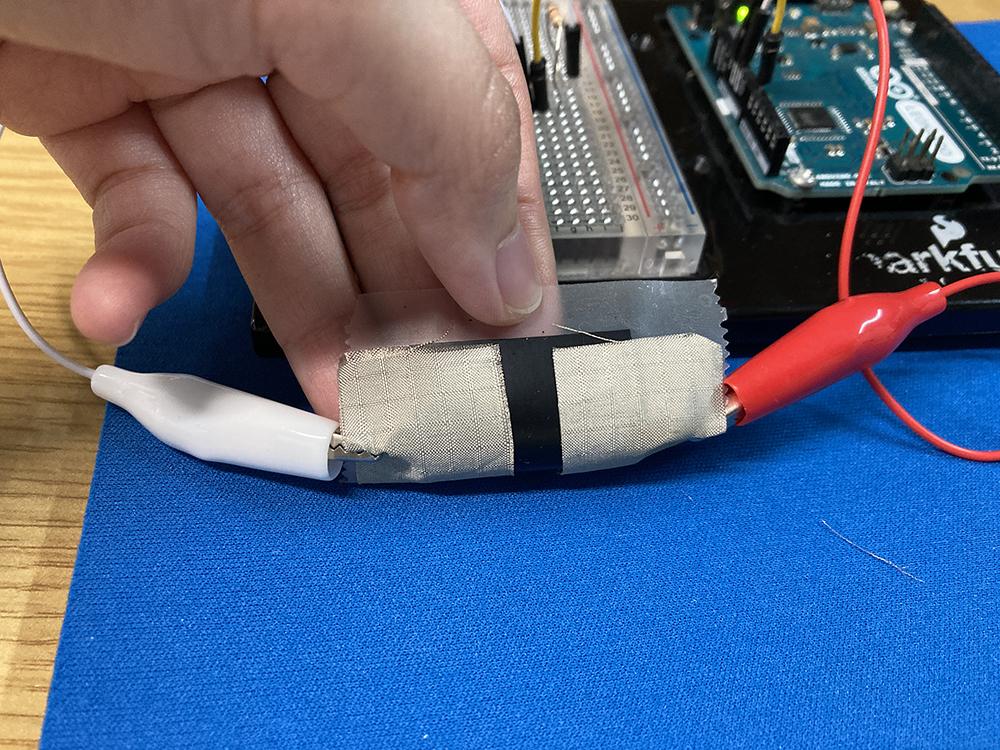
- You need 2 pieces of conductive fabrics and 1 piece of velostat.
- Make sure the 2 pieces of conductive fabrics are not touching each other.
- Tape them down so they are firmly in contact.
- (Optional) Using a piece of non-conductive material as the base to hold everything together, preferably something spongy.
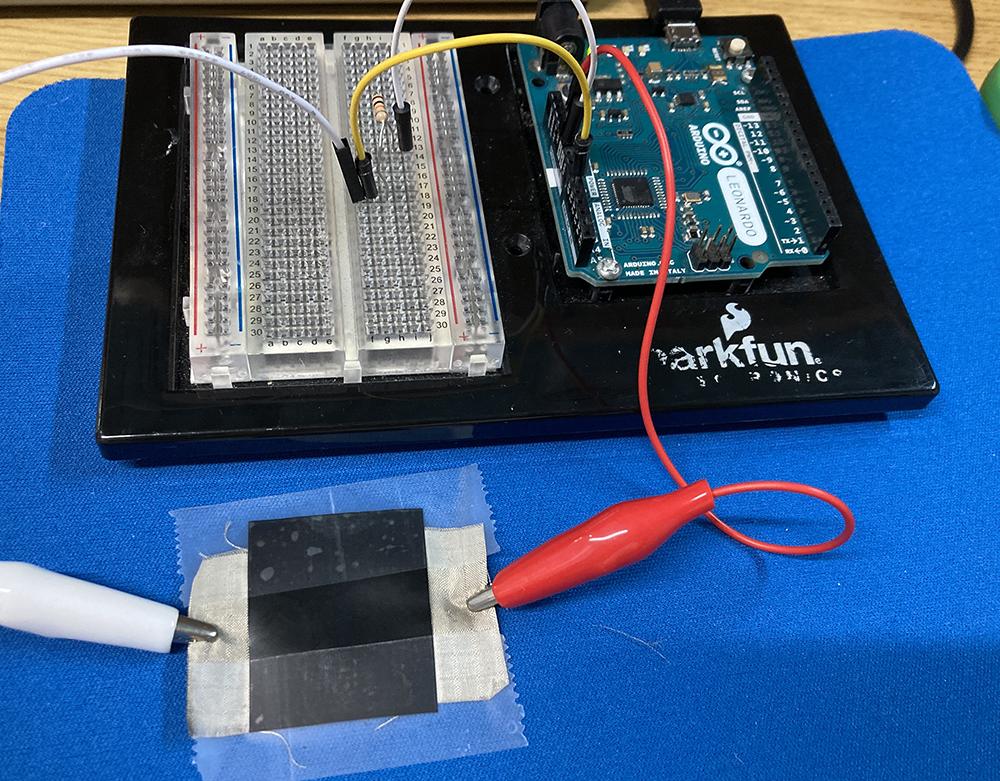
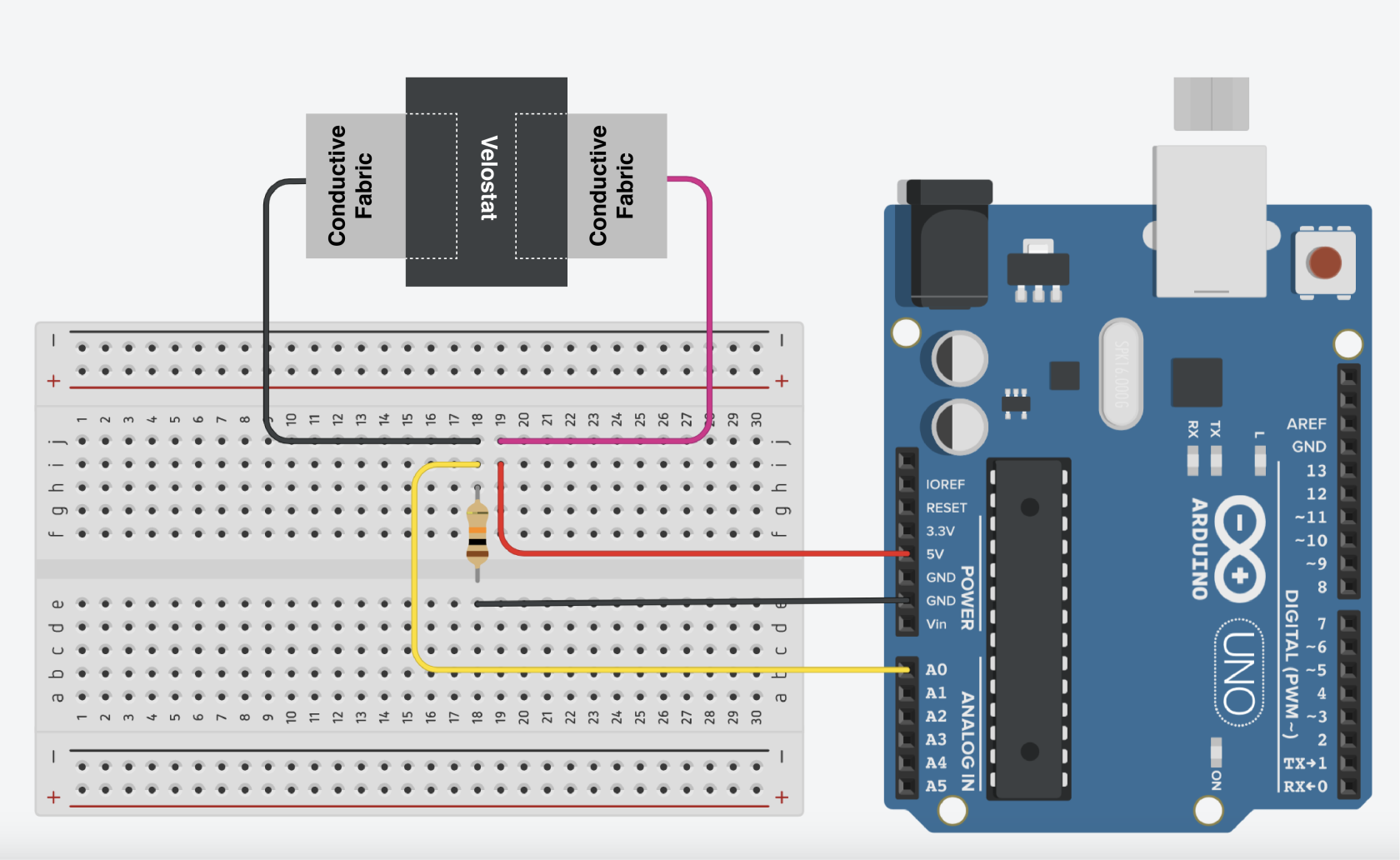
Making a Force Sensor
Wiring
Wiring up the sensor is simple, the sensor is unpolarized so it's doesn't matter which pin to 5V or GND.
- Power (one end to 5V)
- Ground (one end to GND with 10K resistor)
- Signal (GND side to A0)
Code
This example measures the force applied to the velostat.
int sensorPin = A0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // gives analog values for the sensors
Serial.println(sensorValue);
delay (100); // change for the speed of serial monitor
}
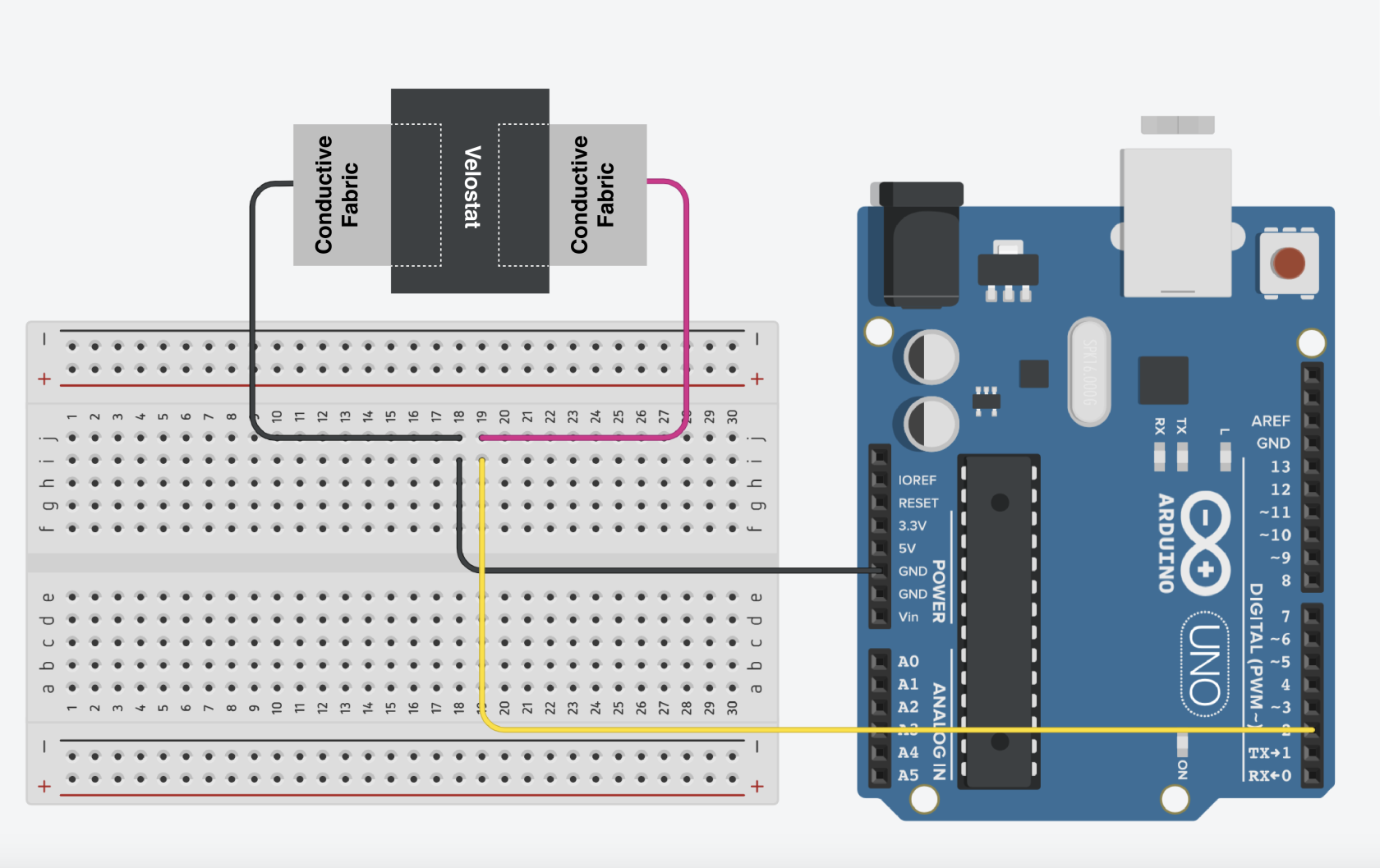
Making a Button
Wiring
We are using a Pull-Up Resistor button set up.
- Ground (one end to GND )
- Signal (one end to A0)
Code
This example detects if the velostat is pressed.
int buttonPin = 2;
int buttonState;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
Serial.println(buttonState);
delay (100); // change for the speed of serial monitor
}