How to control Raspberry Pi Pico via Wifi
PoweringWhat is Wifi
WiFi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a technology that enables devices like smartphones, laptops, and other electronic gadgets to connect to the Raspberryinternet Pior Picocommunicate
with each other without the need for physical cables. It operates by using radio frequency signals to transmit data between devices and a wireless router. The easiestrouter, connected to the internet via a wired connection, acts as a central hub that facilitates communication between devices within its range. WiFi has become a ubiquitous and convenient way for people to poweraccess the internet and share information wirelessly, contributing to the proliferation of wireless connectivity in homes, businesses, and public spaces.
You can create a local wifi network with just powering up a wifi router. When two or more devices (computers, microcontrollers...) are connected to the same wifi network, they can communicate with each other, without accessing the internet. Not all microcontrollers come with a built-in Wifi module so we will be using Pico W (with a built-in wifi module) in this tutorial. But there are plenty of add-ons options you can add to your microcontroller for wifi.
External read for fun:)

What is throughIP theaddress
An cableIP eitheraddress, or Internet Protocol address, is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer ornetwork that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It consists of a phoneseries charger.of Ifnumbers youseparated areby goingperiods, like xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. Think of it as a digital address for your device on the internet. It allows devices to identify and communicate with each other on a wirelessnetwork, design,much youlike a home address allows mail to be delivered to a specific location. IP addresses can usebe batteriesdynamic, asmeaning well.they Thischange tutorialperiodically, or static, where they remain constant. They play a crucial role in routing data packets across the internet, ensuring that information reaches the correct destination.
How to find my IP address
- Google Search - "What's my IP address?"
- Go to Network Preferences (MAC), Wifi Properties (Windows)
- Go to Terminal (MAC) or Command Prompt (Windows) and type in
ipconfig getifaddr en1
Get started
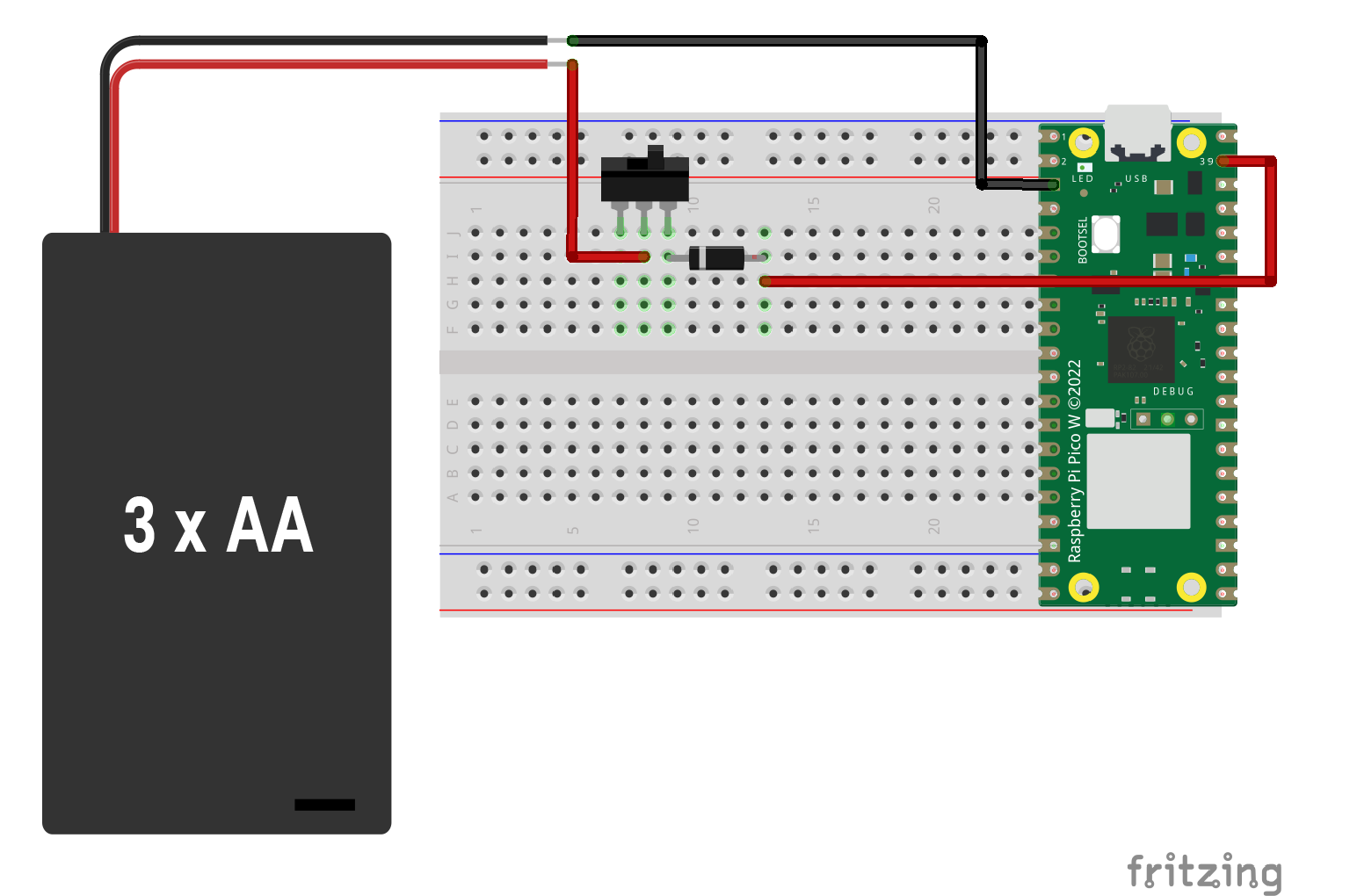
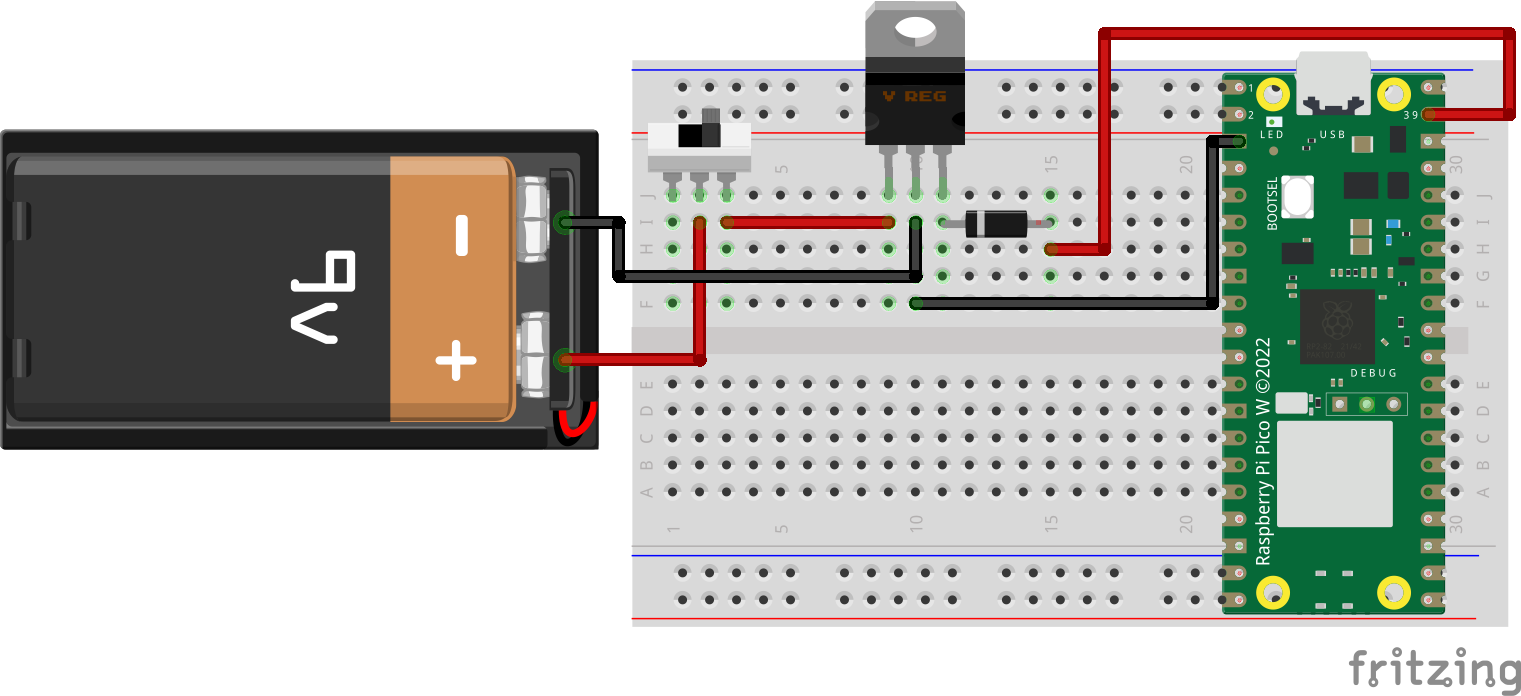
The example code will demonstrateturn on/off the onboard LED on Pico via wifi without an external circuit. See this tutorial to learn how to powerset aup Picoyour withPico. aBefore 9Vyou batterygo orahead, 3there AAare batteries.
Raspberrythings Pithat Picoyou pinout
You haveneed to find out the pinout of the model you are using. The pins you are lookingchange for areyour wifi.
- Change
VSYSssidand,GNDpassword. In this tutorial, a Pico W is used.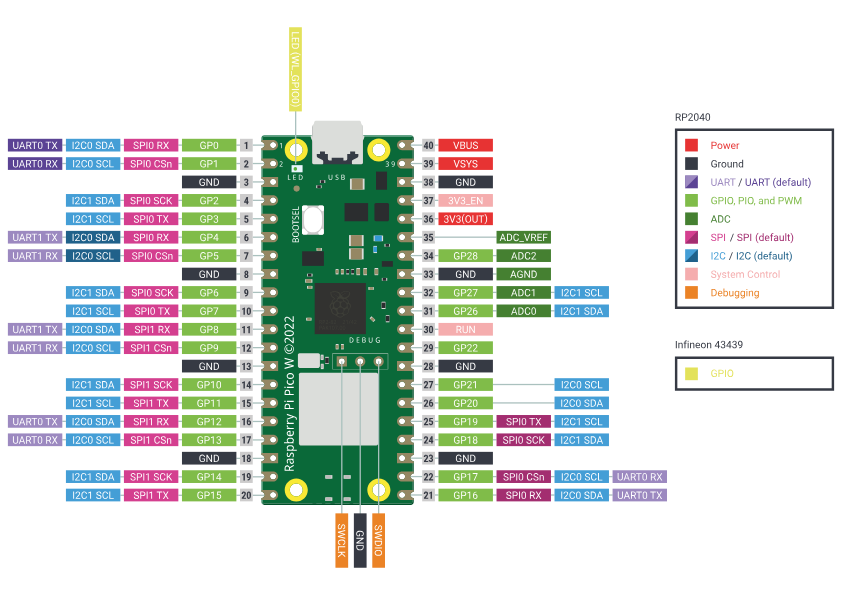
Raspberry Pi Pico's Power NeedVSYS(PIN 39): Pin for main system input voltage. The input voltage can vary between1.8V to 5.5V. This voltage is used by the onboard SMPS to generate 3.3V to power the RP2040 microcontroller and GPIOs.Why these parts are neededSwitch: When we are using batteries to power the microcontroller, a switch is preferred. Some battery holder has a built-in switch which will be more convenient for you. With a switch, you can turn off the Pico when not in use and not drain the battery.LM7805: The LM7805 is a popular voltage regulator integrated circuit (IC). It is a positive voltage regulator that provides a stable and fixed output voltage of +5 volts. It is widely used in electronic circuits to regulate the voltage and ensure a consistent and reliable power supply. It can accept an input voltagein therange of 7V to 35V, depending on the specific model, so you will need this when you are using a power supply with a voltage higher than 5V.- Run
Diode:your- A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flowcode inoneThonny - Find
whileyourblockingIPin theitaddressoppositeThonnydirection.Shell,Insomethingotherlikewords,ipit=acts10.3.15.120 - open up a web browser
- go to
http:// **IP address**/light/onto turn the LED on - go to
http:// **IP address**/light/offto turn the LED off
direction
import network
import socket
import time
from machine import Pin
led = Pin("LED", Pin.OUT)
ssid = 'YOUR NETWORK NAME'
password = 'YOUR NETWORK PASSWORD'
wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
wlan.active(True)
wlan.connect(ssid, password)
html = """<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head> <title>Pico W</title> </head>
<body> <h1>Pico W</h1>
<p>%s</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
max_wait = 10
while max_wait > 0:
if wlan.status() < 0 or wlan.status() >= 3:
break
max_wait -= 1
print('waiting for connection...')
time.sleep(1)
if wlan.status() != 3:
raise RuntimeError('network connection failed')
else:
print('connected')
status = wlan.ifconfig()
print( 'ip = ' + status[0] ) //print your address
addr = socket.getaddrinfo('0.0.0.0', 80)[0][-1]
s = socket.socket()
s.bind(addr)
s.listen(1)
print('listening on', addr)
# Listen for connections
while True:
try:
cl, addr = s.accept()
print('client connected from', addr)
request = cl.recv(1024)
print(request)
request = str(request)
led_on = request.find('/light/on')
led_off = request.find('/light/off')
print( 'led on = ' + str(led_on))
print( 'led off = ' + str(led_off))
if led_on == 6:
print("led on")
led.value(1)
stateis = "LED is ON"
if led_off == 6:
print("led off")
led.value(0)
stateis = "LED is OFF"
response = html % stateis
cl.send('HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\nContent-type: text/html\r\n\r\n')
cl.send(response)
cl.close()
except OSError as ae:
one-waycl.close()
valveprint('connection forclosed')
electric9V battery
Part needed: switch, LM7805 & Any diode
3 AA batteries
Part needed: switch & Any diode