How to use IR Breakbeam Sensor
What is an IR Breakbeam Sensor?
An IR breakbeam sensor is a pair of devices—an infrared (IR) emitter and an IR receiver—that form an invisible beam. When something passes through and blocks the beam, the sensor detects the interruption and triggers an output signal. Know More
Comparing IR Breakbeam Sensor and PIR Sensor for motion detection
| Feature | IR Breakbeam Sensor | PIR Sensor | Which is Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Detection principle | Infrared emitter + receiver; detects beam interruption. | Passive infrared; detects changes in long-wave IR (heat) in its field. | Neutral (different principles) |
| Sensitivity to heat sources | Unaffected by ambient heat or body temperature. | Relies on heat differences; can be affected by temperature changes. | IR Breakbeam |
| Detects cold/heatless objects | Yes — any object that blocks the beam will trigger it. | No — may miss objects with little thermal contrast. | IR Breakbeam |
| Precision / position | Very precise (exact line or plane of detection). | Less precise — detects motion in a broad PIR zone. | IR Breakbeam |
| Response time | Fast / near-instant when beam is interrupted. | Fast for motion but may have slight processing delay. | IR Breakbeam |
| False triggers (small motion / light) | Low — only triggered if beam is physically blocked. | Higher — small animal movement, drafts, or rapid temperature shifts can trigger it. | IR Breakbeam |
| Line-of-sight requirement | Requires clear path between emitter and receiver. | No strict line-of-sight — detects across a field of view. | PIR (for flexibility) |
| Coverage area | Single line/plane — narrow coverage unless multiple beams used. | Wide area coverage with a single sensor. | PIR |
| Power consumption | Typically low to moderate (emitter active). | Typically very low (passive sensor). | PIR |
| Cost & complexity | Generally simple and inexpensive; requires alignment for paired units. | Also inexpensive; easier single-unit installation. | Depends on use (neutral) |
| Best use cases | Object counting, door/threshold detection, conveyor interrupts, tamper lines. | Occupancy detection, motion-triggered lighting, intruder alarms over an area. | Use-case dependent |
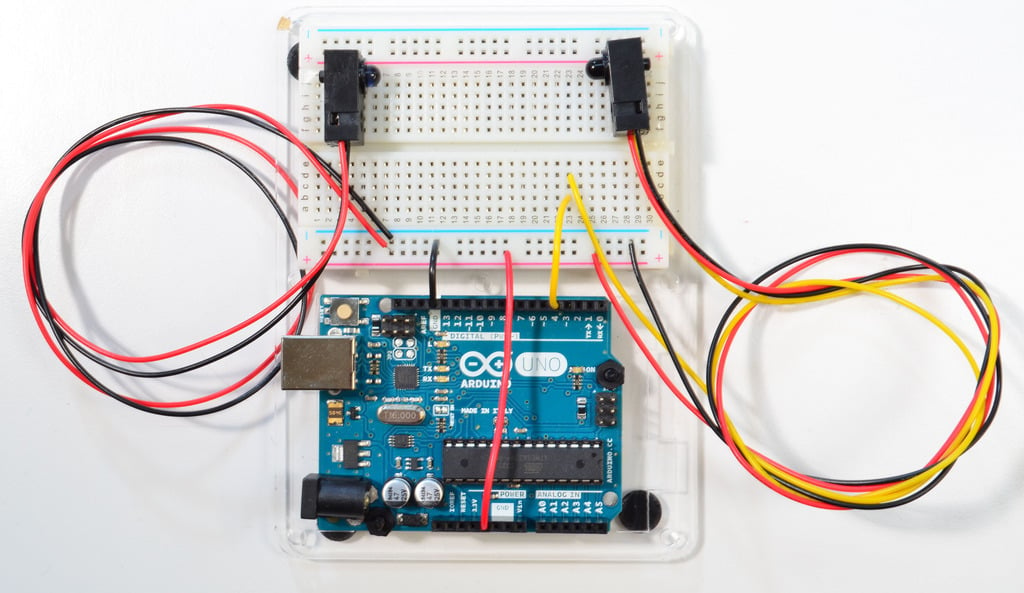
Wiring
Receiver (3 wires)
- Red to 5V
- Black to GND
- White to pin 4
Rransmitter (2 wires)
- Red to 5V
- Black to GND
Get Started
#define LEDPIN 13
#define SENSORPIN 4
int sensorState = 0;
int lastState = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(LEDPIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SENSORPIN, INPUT);
digitalWrite(SENSORPIN, HIGH); // turn on the pullup
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop(){
sensorState = digitalRead(SENSORPIN); // read the state of the pushbutton value:
if (sensorState == LOW) { // check if the sensor beam is broken
digitalWrite(LEDPIN, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(LEDPIN, LOW);
}
if (sensorState && !lastState) {
Serial.println("Unbroken");
}
if (!sensorState && lastState) {
Serial.println("Broken");
}
lastState = sensorState;
}